Individualized Medicine
Healthcare System of the Future:
The Best Possible Treatment for Each Individual Patient
Individualized medicine focuses medical care comprehensively on patient specific needs: tailored therapies instead of one-size-fits-all treatments. Advances in research and technology make it possible to provide treatments that are precisely tailored to the genetic and health characteristics of an individual patient. To provide every affected person with the best possible and most efficient care is the overall goal. As a supplier of specialty pharmaceuticals and compounder of patient-specific therapies, Medios is already paving the way for this development.
CHAPTER 1
The World is Becoming
Increasingly Individual
The megatrend of individualization is changing the world: From custom-made 3D-printed bikes to augmented reality glasses – products and services are increasingly being tailored to individual needs. In medicine, technological advances and research make it possible to provide patient-specific treatments that are revolutionizing our healthcare.
Individualization in Medicine
Healthcare systems face a challenge to address individual patient needs in a more appropriate way. Conventional mass medicine, which still treats patients based on a broad, non-targeted approach, is coming under increasing scrutiny.
Patients with serious diseases such as cancer, multiple sclerosis or hemophilia benefit particularly from more individualized treatment.
More Precise Diagnoses for Targeted Treatment Approaches
Changes in genes, proteins or cellular processes can be analyzed with increasing precision, for example by examining genetic changes in tumor tissue (genetic analysis) or with the help of artificial intelligence, which identifies genetic and molecular patterns. These findings can be used to develop targeted therapies.
Cancer therapy has evolved significantly, and targeted therapy now offers an alternative to the treatment approaches with cytostatic agents. These treatment approaches are based on the molecular, pathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of the tumor, which are identified using diagnostic procedures or biopsy. The treatment objective is to specifically target tumor cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Advanced Therapies include gene therapies, cell therapies and tissue engineered products based on genetic information and biotechnologically processed tissue products. These medicines, also known as Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs), offer individualized and targeted treatment options, e.g. for patients with rare diseases, where conventional therapies fail. One example is oncolytic virotherapy, which is an effective cancer therapy using a special virus that can find and destroy cancer cells in the human body.
Intensive research has helped to harness the body's own defense mechanisms for cancer treatment. Immunotherapies enable the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, even if they have escaped the body’s natural defense mechanism. Today they are a key element of routine clinical practice, for example in lung cancer and certain forms of blood cancer.
Specialty Care is Essential
Successful individualized therapies are based on demanding and intensive cooperation between different healthcare players: health insurers, industry (pharmaceutical companies / Specialty Pharma providers), medical specialists, pharmacies, patient associations, service providers and nursing homes.
The interaction between these players is highly complex and varies depending on the disease pattern. Therefore, seamless collaboration is key to providing individualized treatment.
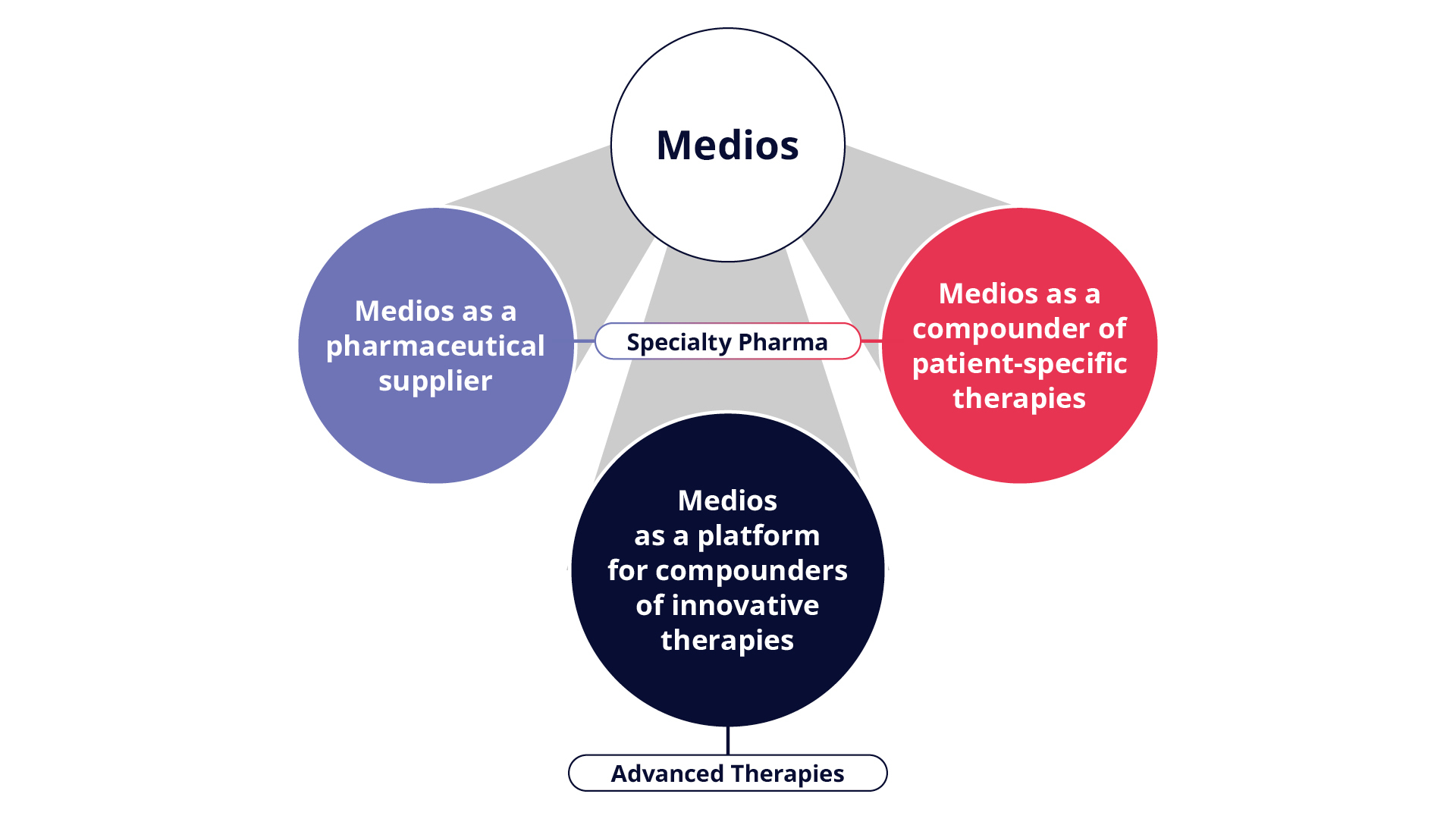
Medios plays a crucial role in individualized medicine. As a Specialty Pharma company, it prepares patient-specific medicinal products and adapts dosages flexibly (blister packaging). Through close collaboration with healthcare players, Medios makes it possible to provide Specialty Pharma while ensuring efficient supply chain. In addition, Medios actively connects key players to make innovative therapies available across Europe and to build a global platform.
Revolution in Healthcare
Challenges such as an aging society, inadequate infrastructure in rural areas and high treatment costs must be addressed.
But individualized medicine promises a revolution in healthcare: To make the most innovative therapies available to everyone, regardless of where they live or their personal circumstances.
CHAPTER 2
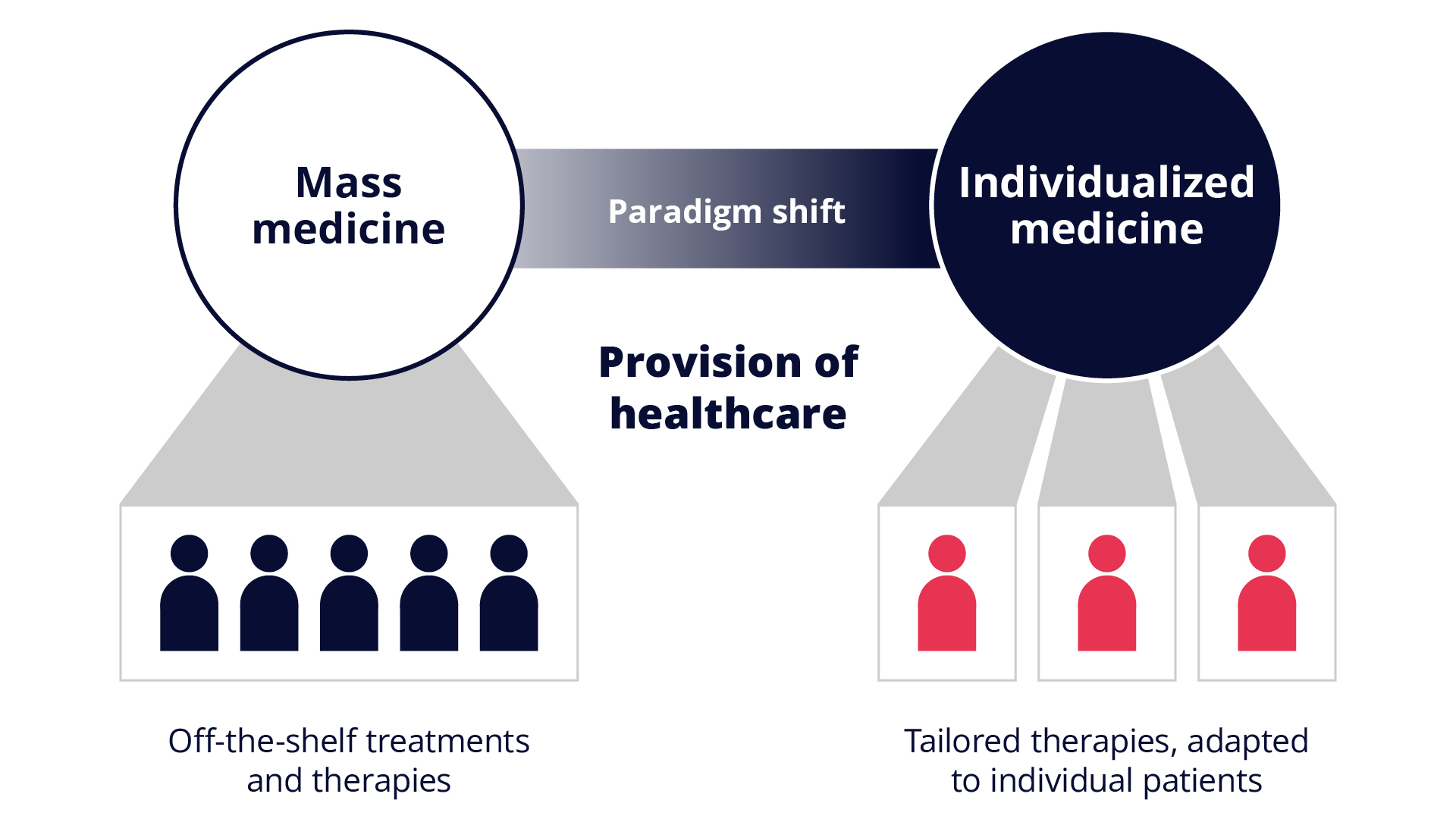
Individualized Medicine vs. Mass Medicine:
What's the Difference?
Mass medicine fights diseases on a large scale. In the 20th century, the standardized approaches of mass medicine (e.g., the use of penicillin or the implementation of randomized trials) led to an increase in life expectancy around the world.
Individualized medicine refers to the full-scale orientation of medicines, therapies and healthcare structures around the individual patient. Related terms include: Specialty Pharma, individualized or personalized medicine.
Significant Limitation of Mass Medicine
Standardized approaches often reach their limitations when managing rare genetic diseases such as Marfan syndrome. Another problem is the gender-specific efficacy of medicinal products: treatments that have been tested primarily on male participants may be less effective in women or lead to unexpected side effects, such as cardiovascular disease.
Advantages of Individualized Medicine
Individualized medicine opens new perspectives on how diseases arise and progress due to the consideration of genetic, biological and environmental factors. This means that medicines, therapies and patient care structures can be tailored more specifically to the needs of individual patients. In this way, individualized medicine enables the provision of targeted and individual care for patients, with the aim of replacing the structures of mass medicine.
Individualized Medicine already Offers Numerous Personalized Options for Tailored Treatments:
In Germany and Europe, more and more specialized centers for individualized medicine are being established. Pharmacogenetic tests can be used to determine optimal medicine dosages, while molecular diagnostics examine genetic changes in the genome and enable targeted therapies. Cancer patients in particular benefit from more effective treatments with fewer side effects (e.g., immunotherapies); there are also treatment advances for infectious diseases such as HIV and hepatitis C.
According to the Robert Koch Institute, more than 490,000 new cases of cancer are diagnosed in Germany each year (RKI, 2023, Cancer in Germany for 2019/2020, 14th Edition). Many of these cases are identified in elderly people with comorbidities leading to treatment complications. Biomarker tests and accompanying diagnostic procedures can help to avoid ineffective therapies and optimize efficacy and tolerability by tailored treatment to the patient.
Although precision diagnostic procedures such as genetic testing are cost-intensive, they enable precise therapy planning and, in the best case, lead to the optimal treatment of seriously ill patients. Despite high initial costs, individualized medicine saves costs in the long term because treatments are precisely tailored, and unnecessary therapies are avoided. Studies such as the scoping review of the International Journal of Public Health (2017) show that personalized therapies, particularly for cancer and cardiovascular diseases, both reduce costs and improve treatment outcomes. Additionally, patients' side effects and hospital admissions were reduced.
However, the efficacy of individualized medicine depends heavily on the investments made by a country's health system. In Germany, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) has been promoting the development of innovative therapies since 2013 with the introduction of the individualized medicine action plan (only in German) and the National Strategy for Gene and Cell-Based Therapies (2022).
To exploit the full potential of individualized medicine, it is necessary to intensify research and development, as well as to provide new patient care networks and ensure the training of qualified professionals. Ultimately, the future of individualized medicine will depend largely on health policy decisions.

HEADLINE EINTRAGEN
Die Überschrift und die Zwischenüberschrift verraten uns, was Sie – die Formularüberschrift gibt dem ganzen den letzten Schliff. Hier können Sie erklären, warum Ihr Angebot so toll ist, dass es sich lohnt, dafür ein Formular auszufüllen.
Denken Sie daran:
- Stichpunkte sind super
- Um Vorteile zu erklären und
- aus Besuchern Leads zu machen.

HEADLINE EINTRAGEN
Die Überschrift und die Zwischenüberschrift verraten uns, was Sie anbieten – die Formularüberschrift gibt dem ganzen den letzten Schliff. Hier können Sie erklären, warum Ihr Angebot so toll ist, dass es sich lohnt, dafür ein Formular auszufüllen.
Denken Sie daran:
- Stichpunkte sind super
- Um Vorteile zu erklären und
- aus Besuchern Leads zu machen.

HEADLINE EINTRAGEN
Die Überschrift und die Zwischenüberschrift verraten uns, was Sie anbieten – die Formularüberschrift gibt dem ganzen den letzten Schliff. Hier können Sie erklären, warum Ihr Angebot so toll ist, dass es sich lohnt, dafür ein Formular auszufüllen.
Denken Sie daran:
- Stichpunkte sind super
- Um Vorteile zu erklären und
- aus Besuchern Leads zu machen.
CHAPTER 3
Europe's Healthcare Systems Are Facing Major Challenges
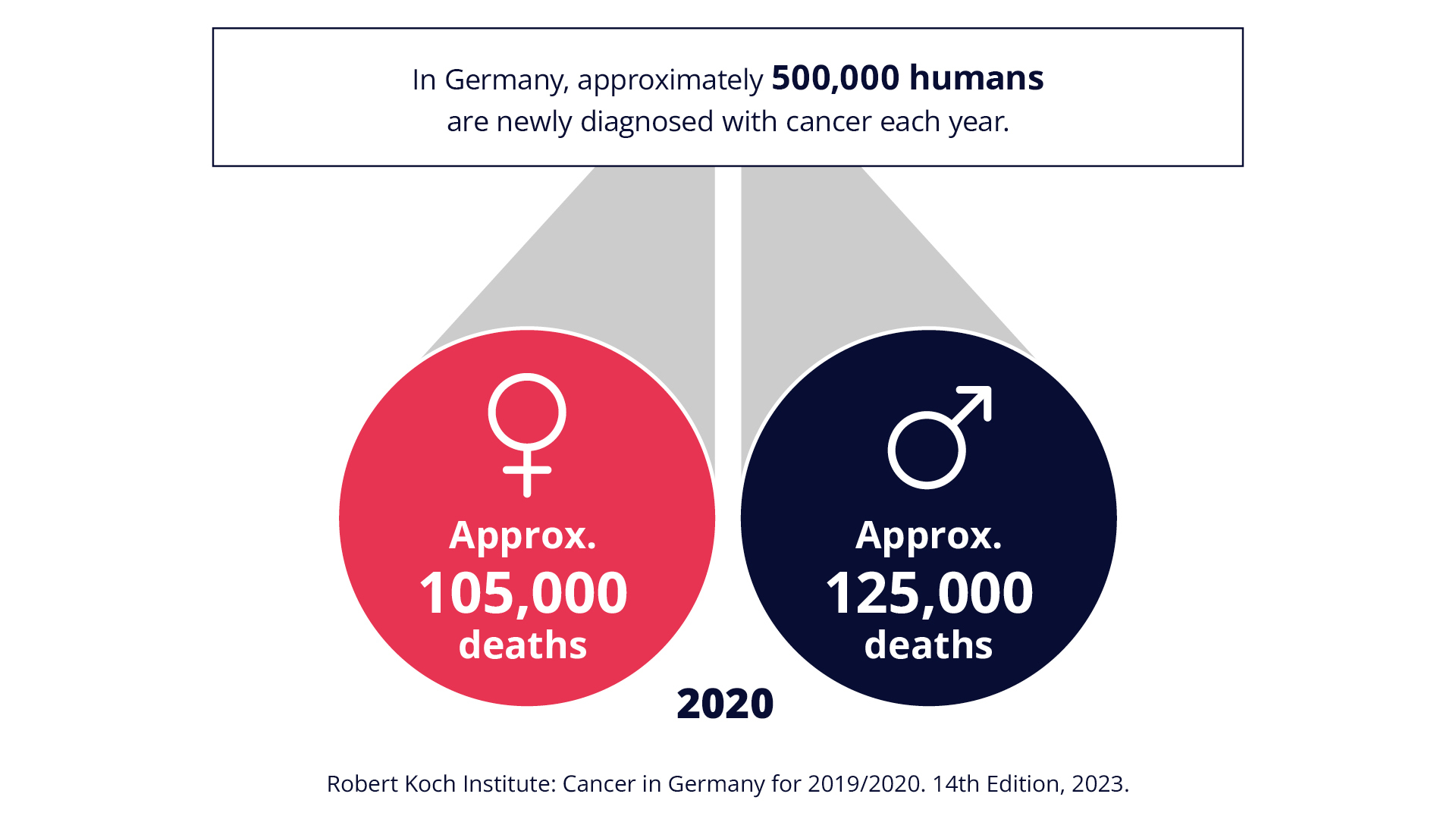
In 2020, approximately 105,000 women and 125,000 men died of cancer, and approximately 500,000 new cases of cancer are diagnosed each year (RKI, 2023, Cancer in Germany for 2019/2020, 14th Edition). Due to demographic changes, not only the number of cancer cases and age-related diseases is increasing, but there is also a greater complexity of the individual disease progression. These developments make innovative treatment approaches increasingly necessary.
Patient-Specific Therapies Improve Medical Care
An increasing number of patient-specific treatment options are becoming available for cancer and other serious and complex diseases.
These therapies consider, e.g. gender-specific differences, body weight and age – key factors for the dosage of pharmacotherapies. This is because every disease progresses differently, and those affected respond differently to the indicated treatments. That’s why healthcare players can now use more targeted “tools” to provide the best possible patient care to the humans behind the diagnoses, reduce side effects, and sustainably improve patients’ life prospects.
The Impressive Potential of Novel,
Individualized Therapies
Severely ill children require individually tailored therapies, as their metabolism and immune systems function differently to those of adults. One example is the CAR T-cell therapy, in which T-cells are taken from the patient, genetically modified to target cancer cells, and then reintroduced into the patient`s blood-stream via an infusion. In 2012, Emily Whitehead, then six years old, was the first child in the world to receive this therapy for her acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Despite severe side effects, which were successfully alleviated by close monitoring and treatment with tocilizumab, the individually tailored therapy resulted in a complete remission. One month after starting treatment, Emily was cancer-free and remains so to this day, over ten years later.
Individualized Medicine: Already Widespread Today
Although novel therapies such as CAR T-cell therapy demonstrate great potential, they have been prescribed sparingly applied due to high costs and possible side effects. Individualized medicine also includes therapies such as cytostatics. Cytostatic agents can be individually tailored based on variables such as height, weight or tumor type and are widely used in cancer treatment. Immunotherapies are also a treatment option for cancer.
However, such patient-specific approaches are not only used in oncology (cancer treatment), but also in other therapeutic areas:
Patient-specific approaches play a central role in the treatment of hemophilia, as demonstrated by the use of the first gene therapy valoctocogene roxaparvovec, which was first administered in Germany in 2023.
Personalized medicine is also successfully used in infectious diseases to treat diseases caused by pathogens. Genetic tests help to predict individual side effects in hepatitis C and HIV patients and to select targeted therapies.
In neurology, medical specialists use individualized therapies such as ocrelizumab for multiple sclerosis (MS), e.g., which consider factors such as age and comorbidities.
In ophthalmology, patient-specific special formulations such as IVOM (intravitreal surgical drug administration) can help slow the progression of degenerative eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Patient-specific therapies offer hope for autoimmune diseases such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis. One targeted therapy option is the treatment with monoclonal antibodies, which can help reduce inflammation associated with such diseases.
Pharmaceutical Requirements:
Medios in Focus
The compounding of patient-specific therapies and specialty pharmaceuticals require the highest pharmaceutical standards. Medios is the leading provider of Specialty Pharma in Germany and operates several GMP sites and cooperates with pharmacies and medical specialists to provide medicines tailored to individual patients.
At Medios, specialty pharmaceuticals and patient-specific therapies are compounded in GMP-compliant cleanrooms, which are subject to strict regulations and controls. Access is strictly regulated and only granted to qualified personnel to ensure the highest quality and to guarantee the protection of both products and personnel.
Close cooperation between all healthcare players is crucial for short-lasting medicinal products. Medios provides patient care throughout Germany in collaboration with a reliable network of pharmacies, medical specialists, clinics, and other pharmaceutical companies. In emergencies, patients can be treated within 60 minutes. Expanding such supply networks is essential to address the challenges of an aging population and the corresponding increase in chronic diseases.
CHAPTER 4
Continuity of Patient Care: Essential for Treatment Success and Patient Safety
“Continuity of care” is paramount in the treatment of diseases. Seamless patient care is crucial to ensure therapeutic success and avoid complications. This requires close cooperation between medical specialists, pharmacies, pharmaceutical companies and specialized providers. Suitable care is based on several fundamental principles:
- Timelines and accessibility: Patients receive quick and easy access to the required treatments.
- Availability: Essential medicines and therapies are available at all times to provide treatments.
- Equality: Regardless of sex, age or professional status, patients with comparable severity of disease receive equally suitable treatment.
- Knowledge-driven treatment planning: The planning and implementation of therapies are based on pro-found medical knowledge. This approach maximizes the efficacy and safety of treatments.
Security of Patient Care in Germany
Ensuring a steady supply of patient treatments is becoming more challenging due to growing supply bottlenecks. In March 2024, the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) reported supply shortages of 138 medicinal products, including the active treatment ingredient tamoxifen, which is mainly used in breast cancer therapy. The main reasons for the supply bottlenecks are production problems, increased demand, and the relocation of pharmaceutical production to sites abroad. The German Federal Government passed the Act to Combat Shortages in Medicines and to Improve Supply (ALBVVG), in particular to improve the availability of medicines for children.
Generics offer a cost-effective alternative to patented medicines, but their production is often no longer profitable. Some compounders are already stopping the production of certain active ingredients, further limiting availability.
Pharmacies are facing major challenges: Access to medicines is becoming more difficult in rural areas, while legal reforms such as changes to pharmacy remuneration reduce resources and make it more difficult for them to provide advice to patients. Affected people who rely on specialty pharmaceuticals require intensive and ongoing appointments. At the same time, the shortage of professional is exacerbating the situation, especially in less attractive regions.
Hospital pharmacies: Reduction from 418 (2010) to 356 (2023).
Public pharmacies: Steady drop in number from 2009, now with only 17,571 operating pharmacies (2023) – the lowest number since the 1970s.
The lack of professionals is increasingly affecting chief physicians and medical specialists. Age-related personnel gaps and insufficient numbers of graduates increase the workload and jeopardize the quality of medical care.
»Despite these developments, the supply of medicines remains secure across the board.«
Specialty Care in an Emergency:
The Fictitious Case of Oncology Patient Stefan Mayer
Stefan Mayer, 68 years old, was diagnosed with advanced-stage colon cancer. The path to the diagnosis was characterized by long waiting times and distance-related barriers. But thanks to a closely networked healthcare system, he was able to receive an individualized therapy.
Read here how modern patient care models and innovative networks made his treatment possible.
In 2023, Stefan Mayer (68 years old, single, retired) began to experience increasing health problems such as lack of energy, weight loss, dizziness and headaches. His general practitioner discovered anemia and elevated parameters of inflammation and referred him to medical specialists. Due to long waiting times in the rural Elbe-Elster district, the diagnosis was delayed. Finally, after an imaging examination in the radiology department of the hospital 60 km away was the suspicion of a malignant tumor confirmed. A two-hour train ride took him to the university hospital in Berlin, where he received the diagnose advanced-stage colon cancer.
An expert panel of specialists (tumor board) recommended an individualized therapy for Stefan Mayer. Under close medical supervision, the treatment demonstrated good results. For further care, he was referred to an oncology practice for regular check-ups. His already taken medication had to be adjusted to his cancer therapy. The patient-specific blister packaging helped him to use his medication correctly.
While taking a walk, Stefan Mayer suddenly felt a violent pain in his lower abdomen. After an emergency referral from his general practitioner, he drove to the specialist oncology practice 30 minutes away. The suspicion: further progression of the cancer. After consultation between the oncologist and the Elbe-Elster Clinic, Stefan Mayer was referred to radiology, where the findings required an adjustment of his therapy.
To ensure that his individualized therapy could be administered the next day, the oncologist immediately contacted a specialized pharmacy which was connected to a regional supply network. The therapy was compounded and delivered within a few hours.
Specialty Care in an Emergency: A Timeline

4:46 PM: Medical prescription was received by the pharmacy, which immediately carried out the legally required plausibility check.

5:13 PM: The pharmacy commissioned a GMP compounding facility in Berlin to compound the therapy.

5:40 PM: The medical specialist practice confirmed the administration of the pharmacotherapy for the next morning.

6:00 AM: Compounding of the therapy started in the cleanroom of the compounding facility.
6:30 AM: Therapy was handed to a logistics employee.

7:00 AM: Delivery to the specialist pharmacy and supply to the medical specialist practice.

8:00 AM: Administration of the treatment to Stefan Mayer.

11:00 AM: Return home with his sister.
Four Approaches for Optimized Specialty Care
Approach 1
Innovative patient care delivery models strengthen medical care in rural areas
In rural areas, long waiting times and limited numbers of medical specialists often make it difficult to quickly diagnose and treat serious diseases such as cancer. Therefore, Medical care centers (MVZs) offer a solution by combining various disciplines under one roof and enabling interdisciplinary care. In addition, telemedicine can overcome geographical distances, enable rapid consultations and relieve local healthcare providers.
Approach 2
Precision medicine and specialty patient care supply of medicinal products are gaining importance
Medical advances, including those made in genetic and molecular diagnostics, have fundamentally improved the treatment of serious diseases. Precision medicine relies on personalized therapeutic approaches based on individual genetic and other molecular factors. At the same time, pharmaceutical solutions such as patient-specific blister packaging enhance the safety and efficacy of the therapy by supporting patients in taking their medication correctly.
Approach 3
Effective patient care: It’s all about networking
Close cooperation between pharmacies, medical specialists, clinics, pharmaceutical companies and specialized providers is essential to ensure fast and effective care. National and regional networks are crucial for the provision of specialty pharmaceuticals.
Approach 4
The network is patient-oriented
Individualized medicine must clearly focus on the patient and consistently tailor treatments to individual factors such as age, general condition and specific disease characteristics. Dedicated experts from various fields – from the treating medical specialists and pharmacy teams to the compounding specialists and logistics partners – work hand in hand to provide patient-specific therapies in a timely manner. Thanks to the network, care can remain patient-oriented at all times.
CHAPTER 5
Medios: Pioneer of Individualized Medicine
The Vision
Enabling the most innovative tailored therapies for everybody across Europe – regardless of where they live or their circumstances – this is the vision at Medios. Patients with rare or serious diseases in particular should receive better treatment options.
The Mission
Medios is actively shaping the progress of individualized medicine and is continuously working on solutions to make patient care more accessible, more efficient, and better tailored to patient needs, for example, by creating a global platform for innovative pharmacotherapies and closing gaps in patient care. With its focus on tailored treatment approaches, Medios is also contributing to the greater cost-effectiveness of healthcare in the long term.
Closing Gaps in Patient Care
Many local pharmacies cannot compound specialty pharmaceuticals for patient-specific therapies as they do not have the required personnel and spatial resources. Medios is closing these gaps by compounding and supplying specialty pharmaceuticals for pharmacies throughout Germany.
Medios as a Driving Force behind Individualized Medicine
Since being founded in 2015, Medios has established itself as a leading provider of Specialty Pharma.
Medios is continuously expanding and now also offers innovative solutions for the development and compounding of patient-specific therapies throughout Europe. With locations in the Netherlands, Belgium and Spain, Medios is implementing its vision across Europe and offers patient-specific solutions for serious and rare diseases.
Network in Germany: Approx. 500 employees, around 900 pharmacies and 700 medical specialists
Europe-wide Network: More than 3,200 pharmacies, 200 hospitals and 500 additional employees
Pharmaceutical Supply: With its specialist wholesale business in accordance with Section 52a of the German Medicines Act (AMG), Medios ensures a comprehensive supply of specialty pharmaceuticals. High storage and delivery capabilities, as well as logistics expertise for temperature ranges from −80°C to +25°C ensure reliable supply for pharmacies and partners.
Quality Standards and Stable Emergency Management: Medios meets the highest quality standards according to GDP guidelines and supports pharmacies with pharmaceutical, logistical, billing and commercial issues. Nationwide emergency depots and a 24/7 hemophilia emergency number (+49 800 5169571) ensure patient care in critical situations.
Compounding of Patient-Specific Therapies: Medios compounds ready-to-use, patient-specific therapies in cleanroom laboratories in strict accordance with GMP guidelines. These include: cytostatics, antibody solutions, parenteral nutrition, antibiotics, ophthalmics, investigational medicinal products, blister packs and pain medication.
Compounding is decentralized and ensures the best possible capacity of all facilities. All compounding steps and the entire supply chain are documented to ensure maximum transparency and the highest quality.
mediosconnect – Digital Solution for Orders and Billing: mediosconnect is a an ordering and billing platform that allows medical specialists to order patient-specific therapies and medicinal products from the pharmacy around the clock. Transparent documentation and direct billing of selective contracts simplify the entire process. Specialist medical practices, specialist pharmacies, health insurance providers and patients benefit equally through less bureaucracy, more security and considerable time savings.
Supply Chain Network: Medios actively promotes collaboration in the Specialty Pharma sector through intensive exchange of experience and knowledge transfer between all players. The network includes pharmacies, medical specialists, pharmaceutical companies, hospitals, health insurance providers, and political actors. The close cooperation strengthens the partnership intelligence and opens new ways of providing patient care.
Every disease progresses differently depending on the individual, and every patient reacts differently to the therapy applied. Therefore, individualized medicine considers the individual clinical picture and the current physical condition of each patient. Especially in rare, complex or chronic diseases, individual therapies often ensure better treatment outcomes.
Germany has high potential for increasing outpatient care: According to an analysis by the Central Institute for Statutory Health Insurance (Zi), 2.5 million inpatient procedures could have been performed on an outpatient basis in 2021. By shifting to the outpatient setting, patient-specific therapies can be organized efficiently and tailored to patient`s needs.
The suitable and safe supply of Specialty Pharma medicinal products requires the cooperation of all actors in the field of patient care, from medical specialists and pharmacies to researchers and companies like Medios. These make a decisive contribution to the development of new treatment options and to increasing efficiency in the supply chain.
Patient-specific therapies are precisely tailored to the specific requirements of each patient. The compounding of such medicinal products is therefore a particularly demanding task. Medios compounds Specialty Pharma medicinal products in state-of-the-art cleanrooms according to international GMP standards. Qualified personnel, validated quality management, and temperature-controlled logistics (-80°C to +25°C) ensure the highest standards.
Innovative medicines require well-thought-out storage and delivery logistics. Medios ensures that specialized pharmacies, medical specialists and clinics can be supplied as quickly as possible, even in emergencies.
Leading the Way in Advanced Therapies and Hemophilia
Medios supports the Federal Government’s National Strategy for Gene and Cell-Based Therapies (2024). Advanced Therapies such as gene therapies and cell therapies offer enormous potential for the treatment of serious and rare diseases. In August 2023, Medios enabled for the first time a hemophilia patient to receive a gene therapy.
Advancing Partnership Intelligence Across Europe
Medios is currently building a European platform that fosters collaboration in the field of individualized medicine. The aim of this platform is to help improve the provision of innovative therapies across the board and to make the benefits of individualized medicine accessible to all patients. Innovation is achieved through intensive exchange of experience, and knowledge transfer between all participants.
Future Perspective
The proportion of elderly people in the population is continuously increasing, and therefore, the need for medical care is rising. At the same time, advances in research and diagnostics enable the detection and treatment of other diseases. As healthcare providers are expected to become more specialized, so is the individualization of pharmaceuticals.
On the Path to Individualized Medicine
Download the compendium here
From patient-specific therapies to gene therapies, innovative treatments are fundamentally transforming healthcare and offering patients new hope, especially for rare diseases. But how can the associated challenges be addressed? How can steady patient care be ensured in the face of supply bottlenecks and a shortage of healthcare professionals? And what role do companies like Medios, which see themselves as pioneers of individualized medicine, play?

This compendium highlights the opportunities and challenges of individualized medicine and shows the impact that individualized medicine has on healthcare today and in the future.